Automating the Integrity Verification Process for Downloaded Software
Wednesday 19th June 2019
I've developed a Bash script that can automatically download and perform integrity verifications for various pieces of software, including Ubuntu ISOs, Kali Linux and some Windows software.
The reason for creating this is to make it significantly easier, more reliable and faster to acquire integrity-checked versions of the software that I regularly use. Previously, downloading and updating this software was a manual process, which is naturally slow and unnecessarily prone to human error.
I've released the script under the MIT license, and it's available on my GitLab profile: https://gitlab.com/jamieweb/dl-integrity-verify
Skip to Section:
Automating the Integrity Verification Process for Downloaded Software ┣━━ Script Demo ┣━━ How does it work? ┣━━ Why is there a need to automate the integrity verification process? ┣━━ Whiptail ┗━━ Conclusion
Script Demo
Upon running the script, a menu will appear allowing you to select which software you wish to download. This is a pre-programmed list of software that the script is capable of performing integrity verifications for:
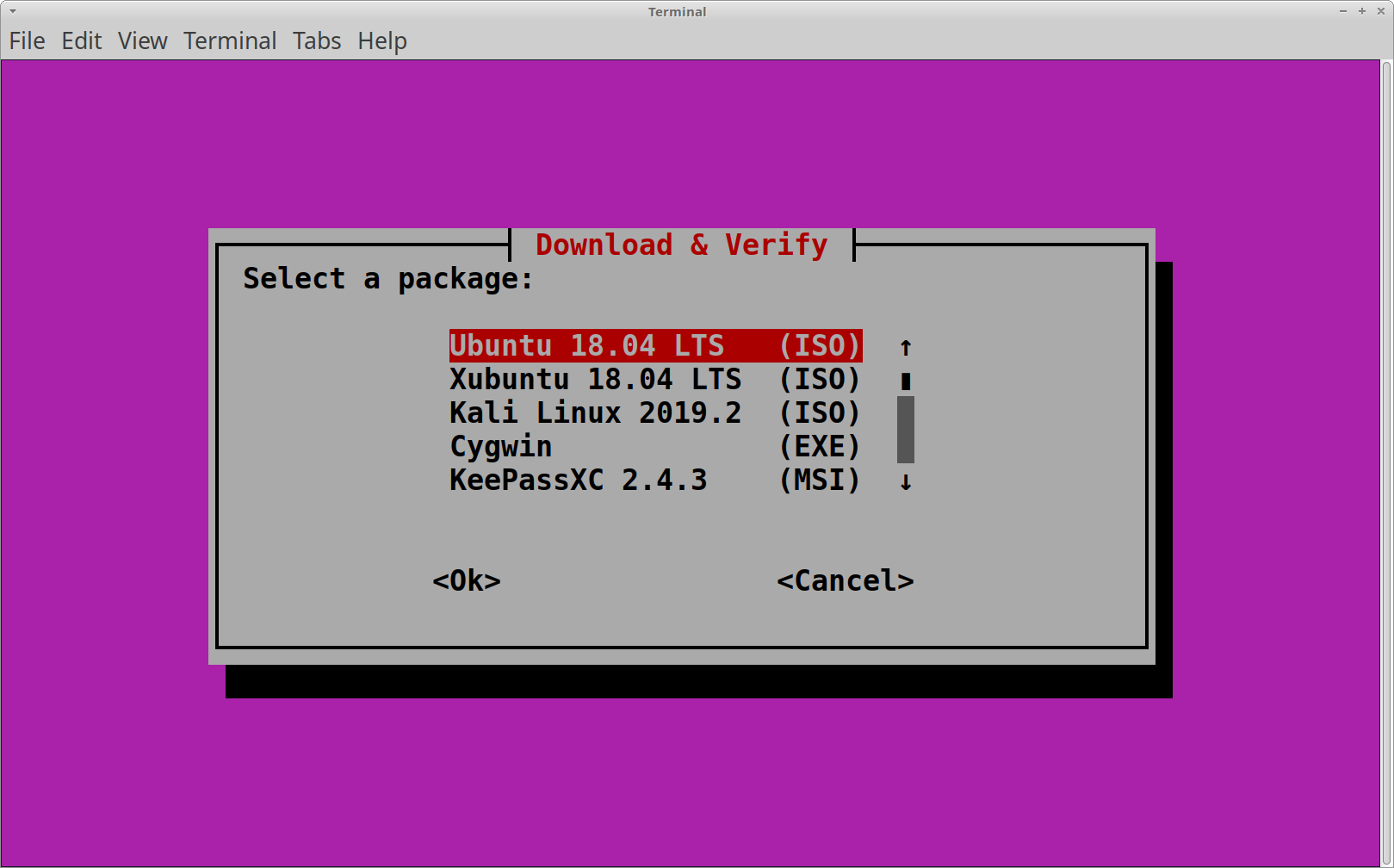
Once you have confirmed your selection, the script perform the actions required to download and verify the file(s). In the case of downloading an Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS ISO, the following is performed:
- Check for existing downloaded files that may be overwritten
- Verify using SHA256 that the download site (scheme, hostname and path) is correct (
http://releases.ubuntu.com/in this case), and hasn't been accidentally modified - Download the required files, including the verification files such as
SHA256SUMSandSHA256SUMS.asc - Verify the detached GPG signatures of the verification files
- Verify the SHA256, SHA1 and MD5 hashes of the downloaded ISO
This will output the following log:
Saving log to 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/VERIFICATIONS' Selected 'Ubuntu 18.04 LTS'. Checking for existing files that may be overwritten by download: ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso: Not Found (OK) SHA256SUMS: Not Found (OK) SHA256SUMS.gpg: Not Found (OK) SHA1SUMS: Not Found (OK) SHA1SUMS.gpg: Not Found (OK) MD5SUMS: Not Found (OK) MD5SUMS.gpg: Not Found (OK) Downloading files... Verifying download site: 'http://releases[.]ubuntu[.]com/' Expected hash: 256b912563ae525d387be32be68fa3f4be7226e5af99f881cf6ab94cacf51fd0 Actual hash: 256b912563ae525d387be32be68fa3f4be7226e5af99f881cf6ab94cacf51fd0 Download site check: OK Downloading 'ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso'... --2019-06-04 22:23:04-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 1996488704 (1.9G) [application/x-iso9660-image] Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso’ ubuntu-18.04.2-desk 100%[===================>] 1.86G 85.5MB/s in 23s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (84.5 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso’ saved [1996488704/1996488704] Downloading 'SHA256SUMS'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/SHA256SUMS Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 202 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS’ SHA256SUMS 100%[===================>] 202 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (24.5 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS’ saved [202/202] Downloading 'SHA256SUMS.gpg'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/SHA256SUMS.gpg Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 916 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS.gpg’ SHA256SUMS.gpg 100%[===================>] 916 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (89.1 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS.gpg’ saved [916/916] Downloading 'SHA1SUMS'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/SHA1SUMS Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 154 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS’ SHA1SUMS 100%[===================>] 154 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (17.6 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS’ saved [154/154] Downloading 'SHA1SUMS.gpg'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/SHA1SUMS.gpg Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 916 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS.gpg’ SHA1SUMS.gpg 100%[===================>] 916 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (99.1 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS.gpg’ saved [916/916] Downloading 'MD5SUMS'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/MD5SUMS Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 138 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS’ MD5SUMS 100%[===================>] 138 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (16.2 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS’ saved [138/138] Downloading 'MD5SUMS.gpg'... --2019-06-04 22:23:26-- http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.2/MD5SUMS.gpg Resolving releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)... 91.189.88.160, 2001:67c:1360:8001::26 Connecting to releases.ubuntu.com (releases.ubuntu.com)|91.189.88.160|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 916 Saving to: ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS.gpg’ MD5SUMS.gpg 100%[===================>] 916 --.-KB/s in 0s 2019-06-04 22:23:26 (101 MB/s) - ‘downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS.gpg’ saved [916/916] Verifying 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS' using signature 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA256SUMS.gpg': gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using DSA key 46181433FBB75451 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: C598 6B4F 1257 FFA8 6632 CBA7 4618 1433 FBB7 5451 gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using RSA key D94AA3F0EFE21092 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key (2012) <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: 8439 38DF 228D 22F7 B374 2BC0 D94A A3F0 EFE2 1092 SUCCESS Verifying 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS' using signature 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/SHA1SUMS.gpg' and key 'ubuntu': gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using DSA key 46181433FBB75451 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: C598 6B4F 1257 FFA8 6632 CBA7 4618 1433 FBB7 5451 gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using RSA key D94AA3F0EFE21092 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key (2012) <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: 8439 38DF 228D 22F7 B374 2BC0 D94A A3F0 EFE2 1092 SUCCESS Verifying 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS' using signature 'downloads/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS/MD5SUMS.gpg' and key 'ubuntu': gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using DSA key 46181433FBB75451 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: C598 6B4F 1257 FFA8 6632 CBA7 4618 1433 FBB7 5451 gpg: Signature made Thu Feb 14 22:53:33 2019 UTC gpg: using RSA key D94AA3F0EFE21092 gpg: Good signature from "Ubuntu CD Image Automatic Signing Key (2012) <cdimage@ubuntu.>com" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: 8439 38DF 228D 22F7 B374 2BC0 D94A A3F0 EFE2 1092 SUCCESS Checking sha256: ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso: OK 22580b9f3b186cc66818e60f44c46f795d708a1ad86b9225c458413b638459c4 *ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso Checking sha1: ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso: OK bcdb9099024c468047f3f31c7d23e68a35ea4de2 *ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso Checking md5: ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso: OK 69809dc7e058b81bc781fe3e24d3204f *ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso
This log serves as evidence for download and integrity verifications for your file. If all of the verifications passed, you'll be able to see this in the log, and know that your file has been verified before using it. If the verifications failed at any stage, the script will have stopped executing, and you can investigate whether there is a security issue, such as an ongoing man-in-the-middle attack, compromised download mirror, etc.
The notable parts of the log are also conveniently saved into the VERIFICATIONS file in the download folder. This is particularly useful for compliance/audit purposes, as it is well-packaged evidence of the integrity verification steps that took place for a particular file.
How does it work?
The script has a pre-programmed list of files that it is able to download and verify. This limitation is by design, as the script is not supposed to be a comprehensive integrity verification tool for any file on the internet. Instead, it's just designed to provide automatic verification for specific files that you want to use.
Each file that you can choose has a list of configuration variables associated with it, such as which download mirror to use, the name of the file on the download mirror, the verification method used, etc.
For example, the configuration variables for the Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS ISO are as follows:
"Ubuntu 18.04 LTS")
file_name="ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso"
dl_site_name="ubuntu-releases"
dl_site_sha256_expected="256b912563ae525d387be32be68fa3f4be7226e5af99f881cf6ab94cacf51fd0"
dl_path="18.04.2"
dl_files=("$file_name" "SHA256SUMS" "SHA256SUMS.gpg" "SHA1SUMS" "SHA1SUMS.gpg" "MD5SUMS" "MD5SUMS.gpg")
verif_method="gpg_signed_hashes_sha256_sha1_md5"
;;
Once a file has been selected from the menu, the first step is to check that the download site (scheme, hostname and path) is correct, by comparing the string (e.g. http://releases.ubuntu.com/) against a SHA256 hash of the known-good version. The reason for this check is to protect against accidental modification/misspelling of the string, as not doing so could result in you accidentally downloading the file from a typosquat/phishing mirror, rather than the real one. In reality this is unlikely to happen, but it's a protection that I wanted and is also useful for compliance purposes, to have a level of cryptographic evidence for where you downloaded the file from.
Next, a check is performed to ensure that the files don't already exist and will be overwritten. If this passes, the files will be downloaded using wget.
The next step depends on the specific integrity verification method in-use for the download that you selected. Some of the pre-programmed packages use GPG signed hashes (e.g. SHA256SUMS.asc and SHA256SUMS), whereas for others, the GPG signature is for the file directly (e.g. setup-x86_64.exe.asc). There is a function for each verification method, the name of which is specified in the configuration variables for the selected package. This function is executed in order to perform the verifications for the package you selected.
If any of these steps fail, the script will terminate and display the relevant error. Otherwise, the verifications completed successfully, providing reassurance that the downloaded package is safe to use.
Why is there a need to automate the integrity verification process?
Software integrity verification is a very important process, so it doesn't make sense for it to be performed manually, not automatically logged and unnecessarily prone to human error.
On Linux systems there is rarely a need to manually download and verify software, as package managers like Apt have integrity verification built in as a fundamental feature. However, in some cases, especially on macOS and Windows systems, it is common practise to download software using a web browser and run it. Most software provides a method to verify the download before running it (e.g. signed DMG files, Authenticode), but in some cases this is not built-in/automatic, so you have to do it manually. Within the IT industry, there is unfortunately a bit of apathy towards taking the time to perform these manual integrity verifications, as some people believe that it's not necessary or 'over the top'.
Package management tools where the integrity verifications are automated and built-in, such as Apt, Brew and Chocolatey are great solutions to this problem (and also solve many others!), as they allow people to acquire and install software, without the hassle and risk of having to download executable installer files using a web browser.
The script I have developed is definitely not any sort of replacement for Brew, Chocolatey, etc - it's just a useful helper script to download the installer files, which may be useful for internal distribution, packaging, etc.
Whiptail
The command-line menus used in the script are provided by Whiptail.
Whiptail is included in most Linux distributions by default, however in some cases only it's predecessor, Dialog, is available. In these cases, the script will fail back to using Dialog. For example, the Cygwin repositories don't have the whiptail package by default, so you have to install dialog instead.
Conclusion
This script will definitely make it much easier for me to securely download Linux ISOs and write them to flash drives to boot from. I also have a Windows 10 machine at work, which is why I have added support for some of the Windows software packages that I use as well.
I'm publishing the script primarily for my own usage, but if somebody else does find it useful, I would definitely be interested in your feedback.